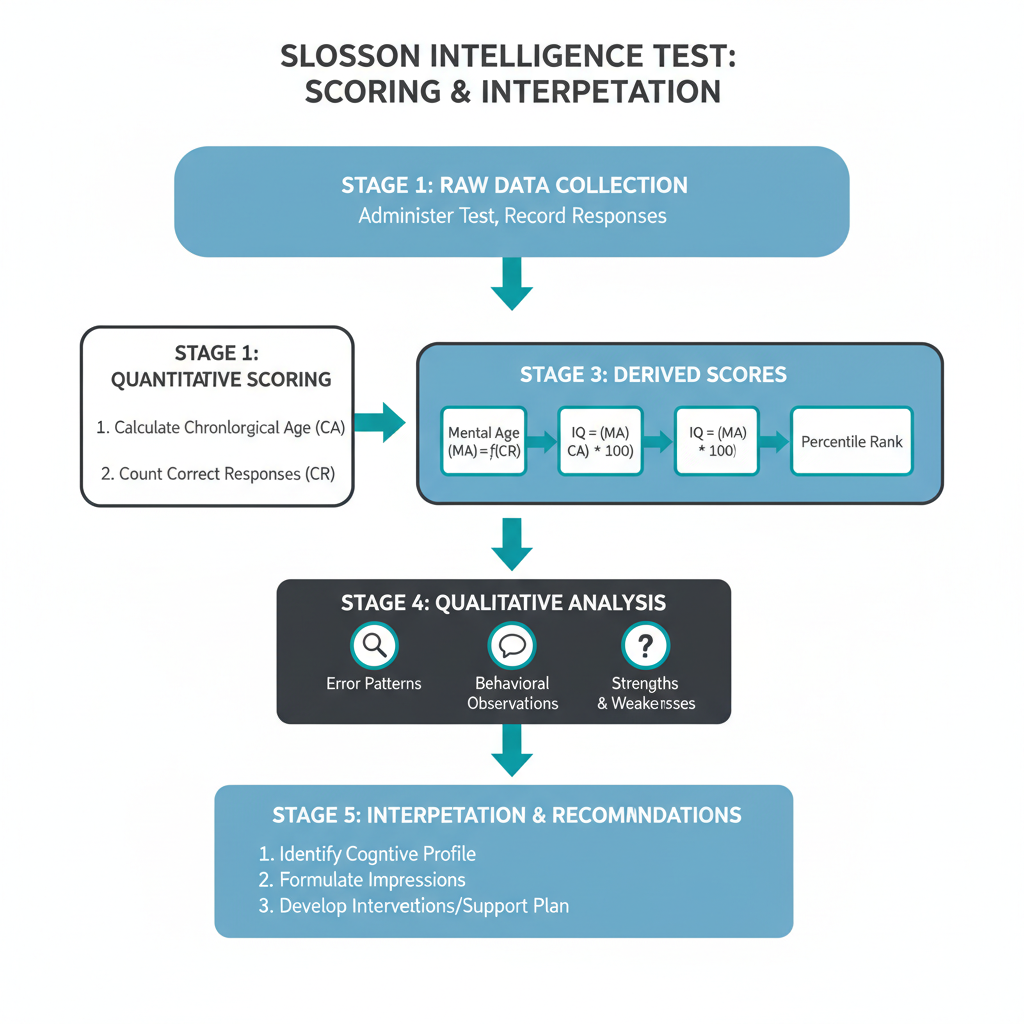
A verbal individual intelligence test is a one-on-one assessment designed to measure a person’s cognitive abilities through language-based tasks. It evaluates key skills such as vocabulary, comprehension, verbal reasoning, and the ability to work with abstract concepts expressed through words to gauge intellectual potential.
Words are the tools we use to form ideas, solve problems, and spark creativity. Language is more than just communication—it’s a core part of how we think and understand the world. Looking at how we use words can tell us a lot about our mental abilities, especially our creative potential. A verbal individual intelligence test does exactly this by providing a structured way to measure these important language-based skills.
This article is your guide to verbal intelligence. We’ll explain what these tests measure and how your language strengths support your unique creative style. We will cover four key areas, from vocabulary to verbal reasoning and reading comprehension, showing what each reveals about your problem-solving abilities. Understanding these aspects of your intelligence will give you practical ways to assess and improve your creativity for personal and professional growth.
What Is a Verbal Individual Intelligence Test?
A verbal intelligence test is a specialized type of test. It measures how well a person can understand, use, and work with language. This test focuses on how you use words and ideas. It provides insights into your language-related thinking skills. In short, it helps us understand how you think with words.
How It Measures Language-Based Skills
These tests look at your language skills in different ways. They measure more than just your vocabulary. Instead, they look at how you understand and use information you hear or read. Verbal intelligence is a key part of our overall thinking skills [1].
Here are the key language-based skills often measured:
- Vocabulary Knowledge: This tests how well you know words and what they mean. A large vocabulary helps you think and express yourself more precisely.
- Verbal Reasoning: This measures your ability to use logic with words. It includes tasks like finding connections between ideas or solving word puzzles.
- Reading Comprehension: This checks how well you understand what you read. It tests your ability to find main ideas, understand implied meanings, and remember details.
- General Information: This measures your general knowledge about the world. It shows how well you learn, remember, and share facts you’ve picked up through language.
By looking at these areas, these tests give a complete picture. They show your skill in communicating with words and in abstract reasoning. Understanding this is important for your personal and professional life.
The Connection Between Verbal Intelligence and Creativity
You may wonder how verbal skills and creativity are linked. The connection is strong and important. Good verbal skills are not just for school. They are a key part of creative thinking and new ideas. Our Creative Ability Test recognizes this crucial relationship.
Here’s how verbal intelligence fuels your creative potential:
- Enhances Divergent Thinking: A large vocabulary and good reasoning skills help you come up with more ideas. You can explore a wider range of possibilities. This helps you connect ideas that seem unrelated, which is key to creative breakthroughs.
- Improves Creative Problem-Solving: Defining a problem clearly is the first step to solving it creatively. Verbal skills help you explain problems, break them down, and share new solutions clearly.
- Boosts Cognitive Flexibility: Creative people can often play with words and look at ideas in new ways. Good verbal skills help you change your point of view easily. This leads to more flexible and creative thinking.
- Helps You Express Ideas: Whether writing a story or explaining a new idea, language is the main tool for creative expression. Clear communication helps others understand your unique ideas.
Ultimately, understanding your verbal intelligence helps you. It helps you see how your language skills can be a powerful tool for creativity. Our platform, Creative Ability Test, provides personalized insights. It shows you how to use these strengths to find new opportunities and improve your innovative thinking.
What are the 4 types of intelligence tests?
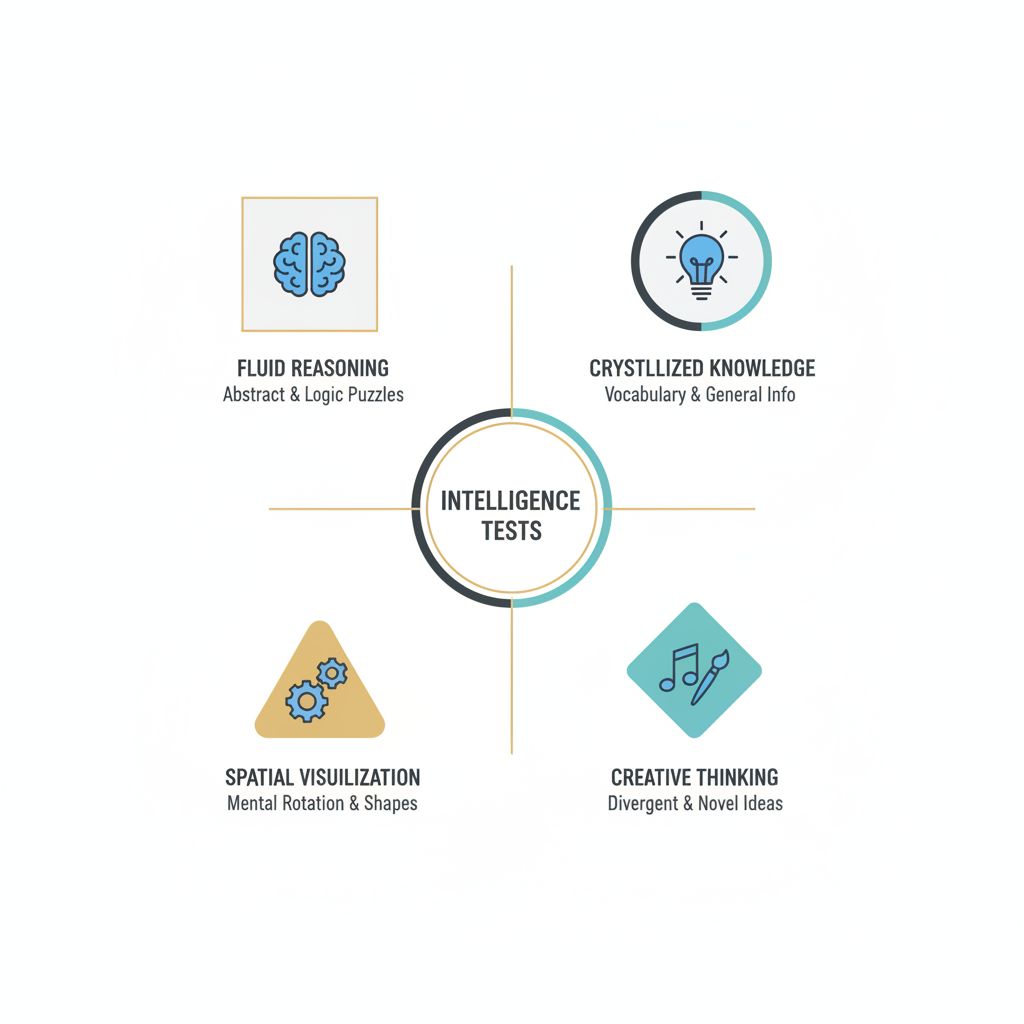
Type 1: Vocabulary and Word Knowledge Tests
These tests check how well you know words, their meanings, and their use in different situations. They measure the size and quality of your vocabulary.
Knowing many words is more than just memorizing them. It shows you can understand subtle meanings and the relationships between words. This is a key skill for communicating clearly.
For creativity, a large vocabulary gives you more ways to express your ideas. You have more words to choose from, which helps you think of new possibilities. This allows you to explain original concepts more clearly and powerfully.
When you learn more words, your thinking becomes more flexible. You can look at problems from different viewpoints. This helps you find creative solutions and tell better stories.
Type 2: Verbal Reasoning and Analogy Tests
Verbal reasoning tests challenge you to see how concepts are related. You use logic and words to solve problems. These tests often use analogies, where you find a link between two words and apply it to another pair.
These tests show how well you think logically and spot patterns. They measure your ability to think about abstract ideas. You also learn how to connect ideas that seem unrelated.
This skill is key for solving problems creatively. A core creative skill is finding similar patterns in different areas. It helps you use a solution from one problem to solve another. This can lead to new and exciting breakthroughs.
Improving your verbal reasoning makes your mind sharper. It helps you face tough problems with a creative approach. You’ll be able to find new ways to solve them.
Type 3: Reading Comprehension Assessments
Reading comprehension tests see how well you understand what you read. They measure your ability to find the main idea and important details. You also practice figuring out information that isn’t stated directly.
These tests show how you process information and think critically. They reveal how well you learn from reading. Being able to absorb new knowledge is very important.
This is especially important for creativity. It lets you research different subjects and combine what you learn in new ways. This information becomes the “raw material” for creative ideas. [2]
By improving your reading skills, you build a strong base of different ideas. This is key for creating new combinations. It also helps you understand complex directions for creative projects.
Type 4: Information and General Knowledge Scales
These tests measure how much you know about the world. They often cover a wide range of topics, like science, history, and current events.
These tests show your general awareness and ability to learn. They also give a sense of your cultural knowledge. It shows how much information you have stored in your mind.
Having a lot of knowledge gives you a mental library of facts and ideas. This internal “database” is great for thinking outside the box. It helps you make surprising connections, which is the foundation of new ideas. You can pull insights from many different topics.
Learning more about the world broadens your viewpoint. It improves your ability to connect things that seem unrelated. This increases your chances of coming up with original ideas and unique solutions for any task.
What Do These Tests Reveal About Your Cognitive Abilities?
Assessing Verbal Fluency and Expression
Verbal fluency is how easily you can find and use words. It also includes how well you express your thoughts. These tests check how fast and accurately you use language.
For example, you might be asked to list as many words as you can that start with a certain letter. Or, you could name items in a specific category. This shows the size of your vocabulary and how fast you can recall information.
Good verbal fluency is key to being creative. It helps you:
- Explain complex ideas clearly.
- Share new ideas effectively.
- Create compelling stories.
- Persuade others with your words.
By understanding your verbal fluency, you can see how well you share your creative ideas with the world. Research shows that language skills, including verbal fluency, are linked to better mental flexibility [3]. This flexibility is a key part of creative thinking.
Improving how you express yourself directly helps you share original ideas. It turns abstract thoughts into clear, powerful messages.
Gauging Abstract Thinking and Problem-Solving
Verbal tests are a great way to measure your abstract thinking. This is your ability to understand ideas that are not physical or solid. It involves finding patterns, making connections, and seeing deeper meanings.
These tests often include analogies or logic questions. You might need to find relationships between words or finish a sequence. This shows how you process information and come up with solutions.
Your problem-solving skills are also closely examined. Verbal tests give you challenges that require logical and critical thinking. You use language to think through possible situations and find good answers.
Abstract thinking and strong problem-solving skills are essential for creativity. They help you to:
- Find the main problem in complex situations.
- Come up with new and different solutions.
- Connect ideas that seem unrelated.
- Think outside the box.
Understanding these mental skills can guide your personal growth. It helps you use your unique thinking style to solve creative challenges. This builds a more flexible and adaptive way of solving problems.
Understanding Your Stored Knowledge
Verbal intelligence tests also check your general knowledge. This includes facts, ideas, and information you have learned over time. It measures your ability to learn and remember things.
Questions in this area might cover different topics, from history to science. They measure your understanding of many subjects. This reflects your curiosity and how much you know.
A large store of knowledge is a powerful tool for creativity. It provides the raw material for new ideas. The more you know, the more connections you can make. You can combine existing ideas in new ways [4].
This includes having a large vocabulary. A bigger vocabulary helps you think in greater detail. It lets you express your ideas with more accuracy and power.
By knowing your strengths in general knowledge, you can use them in creative projects. Continuing to learn new things will naturally spark your creative insights. This leads to more original solutions and fresh thinking.
How Can Understanding Verbal Skills Boost Your Creativity?
Using Language for Divergent Thinking
Good language skills are a great tool for divergent thinking. This is the ability to come up with many different ideas. Instead of finding one right answer, you explore countless possibilities. Strong verbal skills help you put these different thoughts into words.
When you brainstorm, you use words to link ideas. A large vocabulary lets you explore ideas more freely. You can switch from one idea to another more easily. You can also explore small but important differences. This helps you be more creative.
For example, imagine you are designing a new eco-friendly product. With strong language skills, you might list related words like “sustainable,” “repurposed,” “biodegradable,” or “minimalist.” Each word can spark a new design idea. This helps you find more creative options than just the obvious ones.
To boost your divergent thinking with language:
- Practice Word Association: Start with one word. Then, list every related word or idea that comes to mind. Do this without judging your thoughts.
- Engage in Freewriting: Write about a topic for a set time without stopping to edit. Let your thoughts flow freely onto the page.
- Use Idea Journaling: Keep a journal just for new ideas. Write down thoughts, things you notice, and questions every day. Look back at them regularly to find connections.
The Creative Ability Test helps you understand your verbal strengths. It shows how they help you think in different ways. This knowledge allows you to use language to come up with more innovative ideas.
Improving Creative Problem-Solving Through Clearer Communication
Solving problems creatively often means working with others and sharing your ideas well. Strong language skills are key. They help you explain tough problems clearly and describe new solutions with detail.
Imagine you have a great new idea. If you cannot explain it well, it will not have much impact. Clear communication helps others see your vision. It makes sure your creative ideas are heard and valued. It also helps you get good feedback.
Also, just putting a problem into words can be a creative step. How you describe a challenge changes the solutions you think of. Using the right words helps you get to the heart of the problem. It lets you explore it from different angles. This makes your problem-solving more focused and effective.
Think about presenting a new marketing plan. Using clear, simple language helps your team understand the concept and its benefits. Good communication gets everyone on the same page. This makes it easier to put creative ideas into action. Teams with strong verbal communication skills often outperform others in innovation [5].
To get better at creative problem-solving through communication:
- Practice Explaining Complex Ideas: Break down complicated topics into simple terms. Try explaining them to someone who knows nothing about the subject.
- Refine Your Pitches: Learn to sum up your ideas in a short, clear way. Focus on the main value and key benefits.
- Seek and Give Clear Feedback: Use specific language when talking about ideas. Avoid vague comments to create a more helpful environment.
Knowing your communication style is important. The Creative Ability Test can offer insights. This helps you improve your approach and lead more effectively when solving problems.
Unlocking New Ideas with a Richer Vocabulary
Your vocabulary is a toolkit for your mind, not just a list of words. Each word represents an idea, a small difference, or a point of view. A bigger vocabulary expands how you think. It helps you tell ideas apart and understand complex topics better.
Think about the difference between “happy” and “euphoric.” Each word suggests a different feeling. Knowing these differences lets you express yourself better and explore ideas in more detail. This is important for writers, artists, and even scientists.
A large vocabulary helps you connect ideas that do not seem related. It makes your thinking more flexible. You can use different words to describe problems in new ways and create unique comparisons. These are common ways to find breakthrough ideas.
For instance, if you’re stuck on a design, a new word might help. You might be thinking “solid,” but then the word “translucent” comes to mind. This one word can open up new choices for materials and designs. Studies show a strong link between vocabulary size and general thinking ability [6].
To build a richer vocabulary for creativity:
- Read Widely: Read different types of books, authors, and subjects. Note new words and how they are used.
- Use a Thesaurus Thoughtfully: Look up synonyms for common words, but take time to understand the small differences between them.
- Learn Root Words: Understanding Latin and Greek roots can help you figure out the meaning of many new words.
- Engage in Word Games: Puzzles like crosswords or Scrabble are a fun way to grow your vocabulary.
The Creative Ability Test helps you see your verbal strengths. It shows how your word knowledge affects your creative potential. Once you understand this, you can work on building your vocabulary to help you generate fresh, innovative ideas.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some examples of verbal individual intelligence test questions?
Verbal intelligence tests check your ability to understand and use language. These skills are key to expressing creative ideas and solving tough problems. Here are some common types of questions you might see:
- Vocabulary Tasks: You might be asked to define a word. Another common task is to choose a synonym or antonym from a list. A large vocabulary gives you more tools for creative expression.
- Verbal Reasoning and Analogies: These questions ask you to find relationships between words. For example, “Apple is to Fruit as Carrot is to .” (The answer is Vegetable). This tests your ability to see patterns and make connections, which is a key part of creative thinking.
- Reading Comprehension: You read a short passage and then answer questions about its main idea, details, or what it implies. Good comprehension helps you grasp complex information, a skill you need to build on new ideas.
- Information and General Knowledge: These questions might cover a range of topics. For instance, “What is the capital of France?” A wide range of knowledge gives you more building blocks for new ideas. It helps you connect things that don’t seem related.
Understanding these areas helps you use your unique creative strengths. Our platform explores how this kind of mental flexibility can boost your creative potential.
Are there verbal individual intelligence tests specifically for adults?
Yes, absolutely. Many verbal intelligence tests are designed for adults. These tests measure thinking skills in grown-ups. Verbal skills are a key part of intelligence in adults.
A well-known example is the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS). This widely used test includes several verbal subtests [7]. These subtests measure different parts of verbal intelligence, including vocabulary, comprehension, and verbal reasoning.
Adults often take these tests for career development, educational planning, or to better understand their own thinking style. Strong verbal skills are a great help in solving complex problems. They are essential for clearly explaining new ideas and communicating creative visions at work. Understanding your verbal intelligence can show you where you can improve, helping you boost your creative thinking and communication skills.
What is the Binet intelligence test?
The Binet intelligence test was one of the first of its kind, pioneering the field of intelligence testing. French psychologist Alfred Binet and Theodore Simon developed it in the early 1900s. Their main goal was to find schoolchildren who needed extra help in school [8].
A key idea from Binet was “mental age.” This compared a child’s test results to the average results of children at different ages. The first Binet tests focused heavily on verbal tasks to measure reasoning, judgment, and memory.
The test changed a lot in the United States, where it became known as the Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scales. This version is still used today. While it doesn’t measure creativity directly, Binet’s work was revolutionary. It showed that intelligence has many different parts. It helped us begin to understand different thinking skills, including the verbal skills that are a foundation for creative thinking. Our platform builds on this history, exploring how different thinking skills add to your unique creative potential.
Sources
- https://www.apa.org/topics/intelligence/understanding
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8900137/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27040409/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S002210311730032X
- https://hbr.org/2016/11/what-google-learned-from-its-quest-to-build-the-perfect-team
- https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/0956797613487023
- https://www.apa.org/education-career/guide/science-psychology/psychology-assessment
- https://www.britannica.com/science/intelligence-test