A schema test in psychology, such as the Young Schema Questionnaire, is a clinical tool used to identify early maladaptive schemas—deep-seated, negative patterns of thinking and feeling developed in childhood. While used in therapy, the broader concept of ‘schemas’ as mental frameworks is also key to understanding how your unique thinking patterns and assumptions shape your creative problem-solving abilities.
Do some ideas come to you easily, while others feel like a struggle? Your mind is always building invisible guides, or “mental models,” that shape how you see the world. These models affect how you solve problems and how creative you are, influencing everything from daily choices to big breakthroughs. Understanding them is the first step to unlocking your creative potential.
This article explores schema test psychology and how these thinking patterns affect your creative strengths and weaknesses. By learning if your mental models are flexible or fixed, you can better understand how you think. We will guide you through these ideas in a simple, science-backed way, showing you how a structured approach can light up your path to growth.
Get ready to better understand how you solve problems. We’ll show you how to find your own creative patterns and give you practical ways to change them. You will discover clear steps to encourage innovation and personal growth, turning uncertainty about your creative skills into useful self-awareness.
What is a Schema Test in Psychology?
What is a Schema Test in Psychology?
The Clinical Definition of a Schema
In psychology, a “schema” is a basic mental blueprint. Think of it as a shortcut your mind uses to understand the world. Schemas are deep-seated patterns that guide how you think, feel, and act.
Schemas help you quickly sort through new information. They form based on your early life experiences and shape how you see yourself, other people, and the world.
For example, a child who is often praised for trying hard might develop a belief that “effort leads to success.” This belief then shapes their motivation and persistence in the future.
These mental models are powerful. They guide your expectations and reactions to life’s challenges. Schemas are a key idea in cognitive psychology [1].
How Schema Tests Identify Maladaptive Patterns
While schemas are necessary, not all of them are helpful. An “unhelpful schema” is a negative pattern that causes emotional pain or holds you back in life. These patterns often develop when your needs weren’t met as a child.
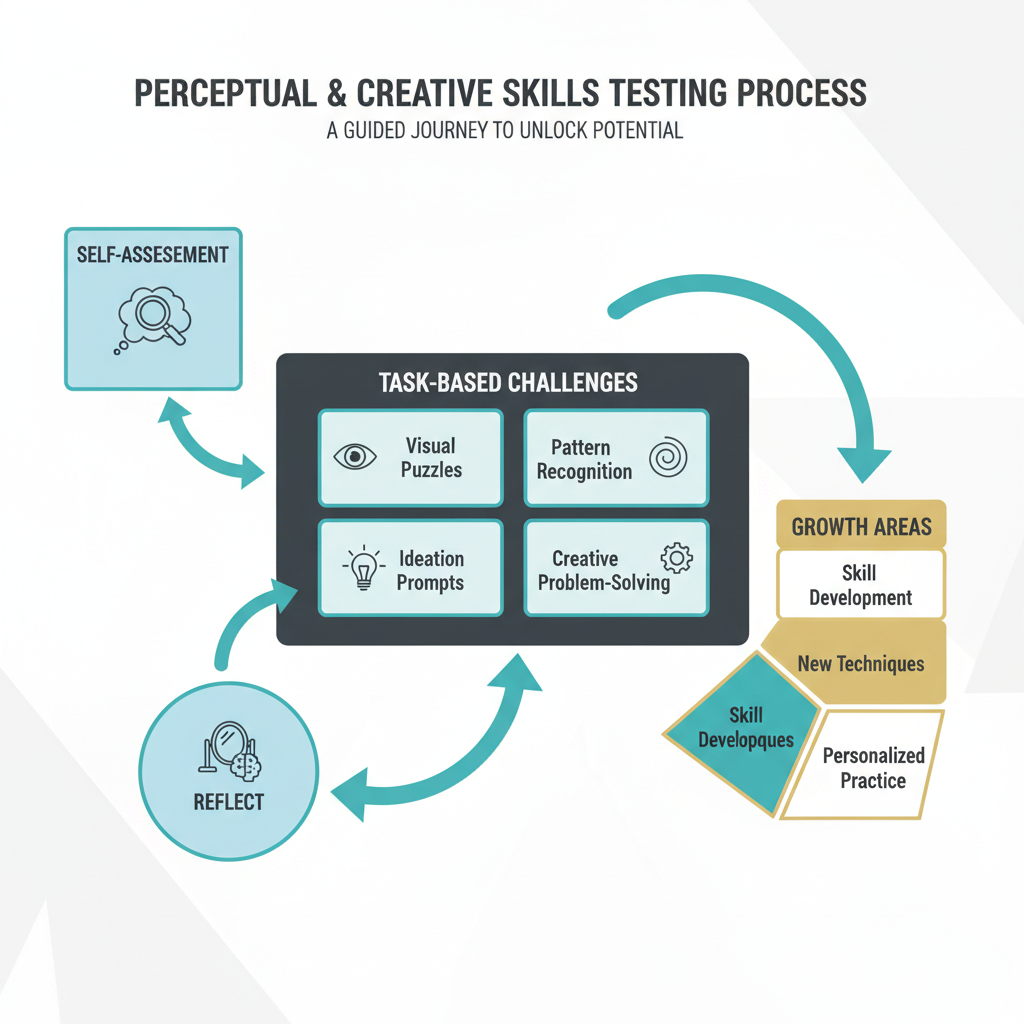
Schema tests are psychological tools that help identify these unhelpful patterns. They are usually questionnaires or surveys that ask about your core beliefs, feelings, and how you tend to act.
The goal is to find repeating patterns that may be holding you back. For example, a test might point to a “defectiveness/shame” schema. This means you might carry a deep, constant feeling of being flawed or not good enough.
Identifying these schemas is the first step toward making a positive change. It helps you understand why certain situations trigger strong reactions. This self-awareness is key to personal growth.
When you understand these unhelpful patterns, you gain the power to challenge them. You can then start to build healthier, more supportive beliefs. Seeing the old pattern is the key to creating a new one [2].
Beyond Clinical Schemas: What Are Your Creative Schemas?
Defining Schemas in the Context of Creativity
In creativity, schemas are your mind’s internal blueprints. They are your usual patterns of thought that shape how you see the world. These mental frameworks guide how you process information, generate ideas, and approach new challenges.
Think of them as mental shortcuts that help your brain manage information. For example, a chef has a “flavor pairing” schema to guide their cooking. A software engineer might use a “problem decomposition” schema to break down complex code. These schemas are not about something being wrong; they are about your unique way of thinking.
Understanding your creative schemas is a powerful tool. It reveals your natural tendencies and shows you where you can expand your thinking. The Creative Ability Test helps uncover these core mental models, showing you how your mind uniquely handles creative tasks.
How Your Mental Models Impact Problem-Solving
Your mental models have a big impact on how you solve problems. They guide your first steps, which can either open up or limit your options. Strong mental models can make hard tasks easier by offering a quick path to a familiar answer. However, they can also cause “functional fixedness” [3]. This means you only see things in their usual roles and miss new ways to use them.
Here’s a simple example. You need to hang a picture. If your mental model for “hanging things” only includes a hammer and nail, you’re stuck without them. A more flexible view might include tape, hooks, or even balancing the frame. This wider view leads to more creative solutions. Your mental models decide your first move and shape the solutions you imagine.
The Creative Ability Test explores these effects. It helps you see your own problem-solving habits. When you understand them, you can choose to explore more options. This lets you tackle challenges with more flexibility and find new, better solutions.
Recognizing Rigid vs. flexible thinking Patterns
Your thinking patterns exist on a scale. On one end is rigid thinking, and on the other is flexible thinking. Both can be useful, but knowing your main style is key to improving.
Signs of Rigid Thinking:
- You stick to familiar methods.
- You find it hard to adapt when things change.
- You prefer outcomes you can predict.
- You struggle to see other points of view.
- You feel uncomfortable when plans change.
Signs of Flexible Thinking:
- You welcome new ideas.
- Adapting to change is easy for you.
- You enjoy exploring different solutions.
- You can easily see a problem from many sides.
- You are open to trying new things and taking risks.
Flexible thinking is essential for creativity and new ideas. It lets you connect unrelated concepts and change course when you face a challenge. Studies show that mental flexibility is a key part of creative intelligence [4].
Think about your own habits. Do you usually fall back on “the way it’s always been done”? Or do you actively look for new approaches? The Creative Ability Test can identify your natural tendencies. It gives you a clear picture of your thinking patterns. This knowledge helps you build more mental flexibility and unlock your creative potential.
How Can You Identify and Test Your Creative Thinking Patterns?

The Role of Divergent and Convergent Thinking
To understand how you think creatively, you need to know about two key ideas: divergent and convergent thinking. They are different, but they work together in any creative project.
Divergent thinking: Generating Ideas
Divergent thinking is all about coming up with lots of different ideas. It’s an open and exploratory process. Think of it as brainstorming without judgment, where you cast a wide net for possibilities. This means thinking outside the box and finding many solutions to one problem.
Key characteristics of divergent thinking include:
- Fluency: Coming up with a large number of ideas.
- Originality: Creating unique and new ideas.
- Flexibility: Shifting between different types of ideas.
- Elaboration: Adding detail to build on and improve ideas.
For example, if asked “How many uses can you think of for a brick?”, divergent thinking pushes you to list everything from building a house to using it as a paperweight or even an art sculpture [5].
Convergent Thinking: Selecting and Refining Ideas
After you have a lot of ideas, convergent thinking helps you choose the best one. This process is focused on finding the single most fitting solution. It uses evaluation, critical thinking, and logic. You take your wide range of ideas and shape them into something that works.
Convergent thinking helps you to:
- Analyze and weigh your options.
- Find patterns and connections.
- Use logical reasoning.
- Select the best or most practical solution.
A strong creative process uses both. Divergent thinking creates options, and convergent thinking turns those options into reality. Knowing which style you prefer can reveal a lot about how you create.
Assessing Your cognitive flexibility and Openness
Besides divergent and convergent thinking, two other traits are key to your creativity: cognitive flexibility and openness to experience. These qualities affect how well you handle new situations and ideas.
Cognitive Flexibility: Adapting Your Mindset
Cognitive flexibility is your brain’s ability to switch between different ideas or tasks. It helps you adjust your thinking when you get new information or when things change. This skill lets you see problems from new angles and try a different approach if your first one doesn’t work.
High cognitive flexibility often means you can:
- Pivot easily between different ideas or solutions.
- See problems from various viewpoints.
- Learn quickly from new experiences.
- Get past mental roadblocks with ease.
In contrast, rigid thinking makes it hard to break free from old habits, which can block new ideas.
Openness to Experience: Embracing the New
Openness to experience is a core personality trait that is closely tied to creativity. It reflects your willingness to explore new ideas, feelings, and experiences [6]. People who are high in openness tend to be curious, imaginative, and have an appreciation for art and beauty.
This trait directly boosts your creativity by:
- Encouraging you to explore unusual ideas.
- Fostering a desire to experiment.
- Making you more receptive to different views.
- Driving a need for new and stimulating experiences.
Looking at these traits helps you see how well you welcome change and new information. They are essential for creative growth and for solving problems well.
Discovering Your Strengths with the Creative Ability Test
If you want to understand your own mix of creative skills, an objective test is the best way. The Creative Ability Test offers a science-backed method to learn about your personal creative style.
How the Test Works
Our 30-question test is designed to measure several sides of your creativity. It gives you a deeper look than just your own opinion, with insights into your:
- Cognitive flexibility.
- Problem-solving approaches.
- Openness to new experiences.
- Ability to both generate and select ideas.
The test is based on proven creativity research to ensure your results are reliable and meaningful.
Personalized Insights for Growth
When you finish the test, you’ll get personalized feedback. Your report will explain your creative strengths and show you where you can improve. It’s more than a score—it’s a guide for your growth.
You will gain:
- Actionable self-awareness: Get a clear picture of your unique creative style.
- Growth strategies: Get practical tips to improve your creative skills.
- Application insights: Learn how to use your creative strengths in real life.
The Creative Ability Test helps turn confusion about your creative skills into clear, useful knowledge. It helps you move from unpredictable results to a solid plan for improvement. Start your journey to discover and boost your creative abilities today.
How Do You Reshape Schemas to Enhance Creativity?
Practical Steps to Challenge Rigid Thinking
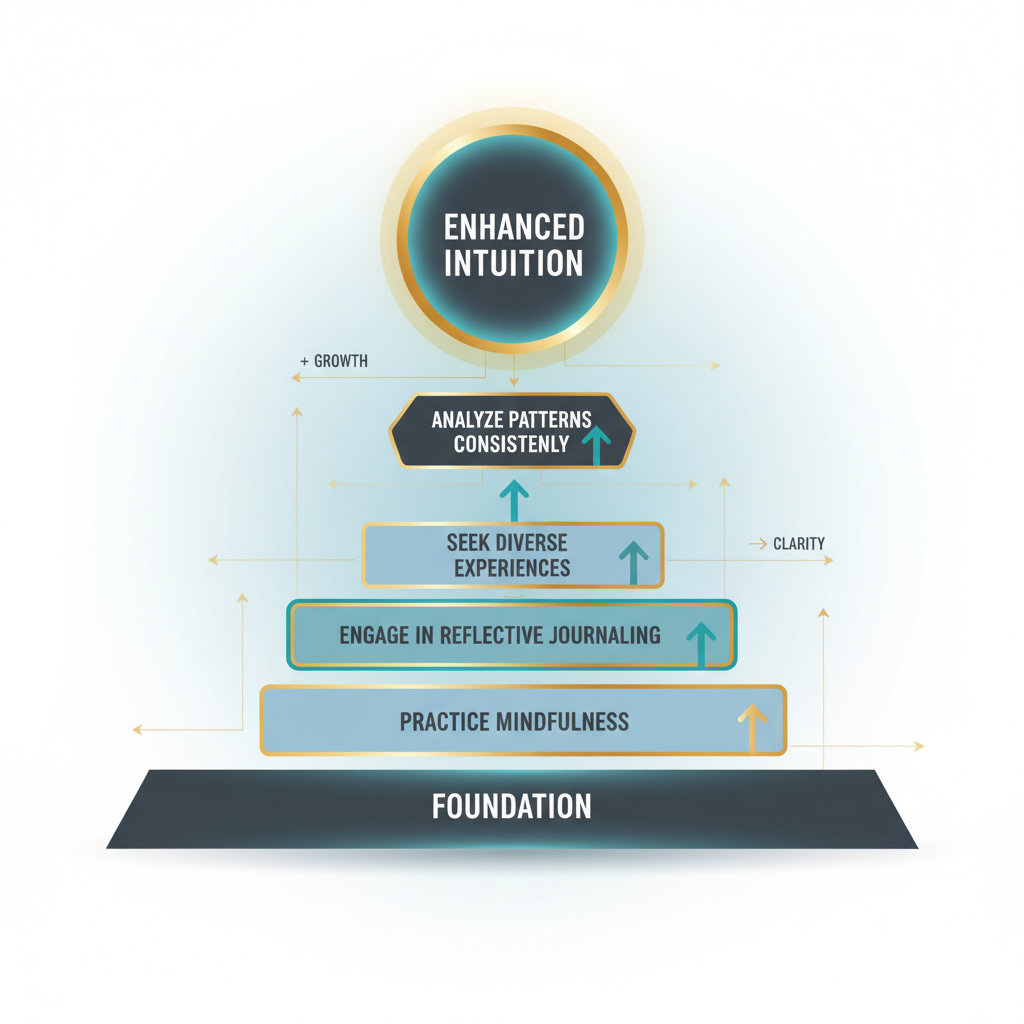
Knowing your mental habits is the first step to unlocking your potential. But just knowing about them isn’t enough. You have to actively challenge your rigid thinking. This process starts with self-awareness.
Rigid thinking often comes from old mental shortcuts. These shortcuts may have helped you in the past, but they can block new ideas now. The key is to notice when you’re using them.
- Question Your Assumptions: Many creative blocks come from beliefs you’ve never questioned. Ask yourself: “Is this truly the only way?” or “What if I assume the opposite?” This simple act can open new paths.
- Actively Seek New Perspectives: Go out of your way to find different viewpoints. Read books you wouldn’t normally choose. Talk to people with different backgrounds. This expands how you see the world.
- Embrace “What If” Scenarios: Playfully explore “what if” situations. Imagine solutions with no budget, no time, or unlimited resources. This practice helps you think in new directions.
- Break Down Problems: Big problems can feel overwhelming. Divide them into smaller, more manageable parts. Each piece might need a different solution. This keeps one rigid habit from taking over.
- Practice Mindful Observation: Notice how you react to new ideas. Do you dismiss them quickly? Or do you pause to consider their value? Being more self-aware helps you catch rigid responses early [7].
By using these steps regularly, you can break down inflexible thought patterns. You’ll train your mind to be more flexible and creative.
Strategies for Building More Flexible Mental Models
Challenging rigid thinking is an ongoing process. Once you find areas to improve, you need ways to build more flexible ways of thinking. This means forming new habits and mental approaches.
Flexible thinking helps you adapt quickly. It helps you find new solutions when things change. Here are some proven strategies:
- Engage in Divergent Thinking Exercises: These exercises push you to explore many possible solutions. Brainstorm ideas without judgment. Use tools like mind mapping or the SCAMPER method (Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to another use, Eliminate, Reverse) to come up with varied concepts.
- Learn Something New Regularly: Learning a new skill forces your brain to make new connections. This could be a new language, a musical instrument, or a coding skill. This directly improves your mental flexibility.
- Seek and Embrace Constructive Feedback: Feedback gives you an outside view of your ideas. It helps you see your own blind spots. See criticism as a chance to make your ideas better.
- Practice Metacognition: This means “thinking about your thinking.” Regularly think about how you solved a problem. What thinking patterns did you use? How could you have done it differently? This helps you better control how you think [8].
- Cultivate a Growth Mindset: Believe that you can improve your skills with effort. This mindset helps you keep going. It helps you learn from challenges instead of avoiding them.
The Creative Ability Test gives you personal insights into your thinking flexibility. It shows you which areas to focus on for the biggest impact. This test helps you create a plan for your own growth.
Applying New Creative Frameworks to Real-World Challenges
Changing your thinking habits isn’t just a theory. The real value is using these new, flexible ways of thinking on real-world problems. Putting what you know into action is how true innovation happens.
When you face a challenge, your new thinking habits give you a fresh perspective. You can see opportunities where others only see roadblocks. This leads to better and more creative solutions.
- Re-frame the Problem: Instead of focusing on symptoms, look for the real causes. Define the challenge in a few different ways. For example, change “how to make people buy more” to “how to help people fulfill their needs.” This simple change can reveal completely new solutions.
- Adopt an Iterative Approach: Don’t try to be perfect on the first try. Create small versions of your idea to test. Get feedback, and then make improvements. This process helps you learn and adapt as you go.
- Collaborate with Diverse Teams: Work with people who have different skills and backgrounds. Their unique ways of thinking will challenge and improve your own. This teamwork often leads to breakthrough ideas.
- Use Storytelling to Present Solutions: New ideas can be hard for people to accept. Tell a story about your solution. Explain the problem, the journey, and the positive result. This makes your ideas easier to understand and more convincing.
- Leverage Personalized Insights: The Creative Ability Test gives you a clear map of your unique creative strengths. Use this information to choose the best approach for you. For instance, if you are good at coming up with many ideas, focus on that. If you are better at choosing the best idea, focus on that skill.
By using these strategies, you’ll gain confidence in your creative skills. Your creativity will become more consistent and you’ll see real growth. The Creative Ability Test provides the starting point, with personal, practical tips to guide you in solving problems and creating new things.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a maladaptive schema test in psychology?
A maladaptive schema test is a tool used in psychology. It helps find negative patterns in how you think and act. These patterns, called schemas, usually start in childhood. They can change how you see yourself and the world around you. These schemas often cause problems in relationships and everyday life [9].
While these tests are mainly for diagnosis, anyone can benefit from understanding their schemas. These fixed ways of thinking can hold back your creativity. For example, a belief that you will fail might keep you from trying new things. Our Creative Ability Test is different. It focuses on your creative thinking patterns. It helps you find and build on the habits that boost your creativity and growth.
Can you take a schema test online for free?
Yes, you can find many free, informal “schema tests” online. But it’s important to know what they can and can’t do. Most free quizzes are just for self-reflection. They are not meant for a clinical diagnosis or for deep psychological information. For that, you need a formal test from a professional. A professional can guide you and explain the results to give you a full picture of your schemas.
If you want to understand your creative thinking patterns, our Creative Ability Test is a better fit. It’s a 30-question test based on science. You get feedback tailored just for you. The test looks at your creative strengths, how you adapt your thinking, and your problem-solving skills. While it isn’t free, it gives you useful tips. You get deep, personal insights to improve your creativity, which is more practical than a generic quiz.
What kind of questions are on a schema test in psychology?
Questions on a clinical schema test ask about your deepest beliefs, feelings, and actions. They explore how you feel in different situations and how you see yourself, other people, and the future. You might see statements like, “I don’t fit in,” or “I am often criticized” [9]. Your answers help find schemas like abandonment, defectiveness, or a feeling of not getting enough emotional support.
In contrast, the Creative Ability Test asks about your creative thinking. It looks at how you handle problems and come up with ideas. Our test looks at things like:
- Divergent Thinking: How easily can you find many solutions to a problem?
- Cognitive Flexibility: Can you change your point of view or adapt to new details?
- Problem-Solving Approaches: Do you like using logical steps or following your intuition?
- Openness to Experience: Are you curious about new or unusual ideas?
These questions give you a clear picture of your creative strengths. They show you your main creative styles. This knowledge can help you use your skills to grow at work and in your personal life.
Sources
- https://dictionary.apa.org/schema
- https://www.schematherapy.com/the-schema-therapy-model
- https://www.simplypsychology.org/functional-fixedness.html
- https://psycnet.apa.org/record/2012-30040-001
- https://psychology.iresearchnet.com/experimental-psychology/cognition/divergent-thinking/
- https://www.simplypsychology.org/big-five-personality.html
- https://greatergood.berkeley.edu/topic/mindfulness/definition
- https://www.apa.org/education-career/guide/science-education/metacognition
- https://schematherapy.com/wp-content/uploads/The-Schema-Therapy-Model.pdf