A multi intelligence test is an assessment based on Howard Gardner’s theory that humans possess several distinct types of intelligence beyond a single general ability (IQ). These tests evaluate an individual’s strengths across different domains—such as linguistic, logical, spatial, and interpersonal—to provide a holistic view of their cognitive capabilities for personal and professional development.
Many of us grow up thinking intelligence is a single number, like an IQ score. But we all know people who are smart in different ways. Some are good with words, others with numbers, and some are great at understanding people. What if intelligence is really a mix of different abilities? This article explores the idea of multiple intelligences, a concept that can help you understand your unique strengths and creative potential.
Developed by Harvard psychologist Howard Gardner, the theory of multiple intelligences suggests there are many “kinds of intelligence” that go beyond just book smarts. Understanding your dominant intelligences isn’t about labeling yourself; it’s about getting to know yourself better. It helps you see how you naturally process information, solve problems, and think creatively, whether you’re “word smart,” “picture smart,” or “people smart.” This insight is a powerful tool for personal growth, allowing you to use your natural gifts in new and effective ways.
This guide will walk you through Gardner’s theory and each of the nine types of intelligence. By understanding them, you’ll get a clearer picture of how you think, discover what makes you creative, and learn simple strategies to build on your skills. Prepare to see your intellect in a whole new way, empowering you to move forward with greater confidence in your personal and professional life.
What Is a Multi Intelligence Test?
Beyond the traditional IQ test
For years, intelligence was measured by a single score, usually from an IQ test. But the traditional IQ test has limits. It mainly focuses on logical reasoning and verbal abilities, often missing other important human skills. Because of this, many people felt their real talents were overlooked.
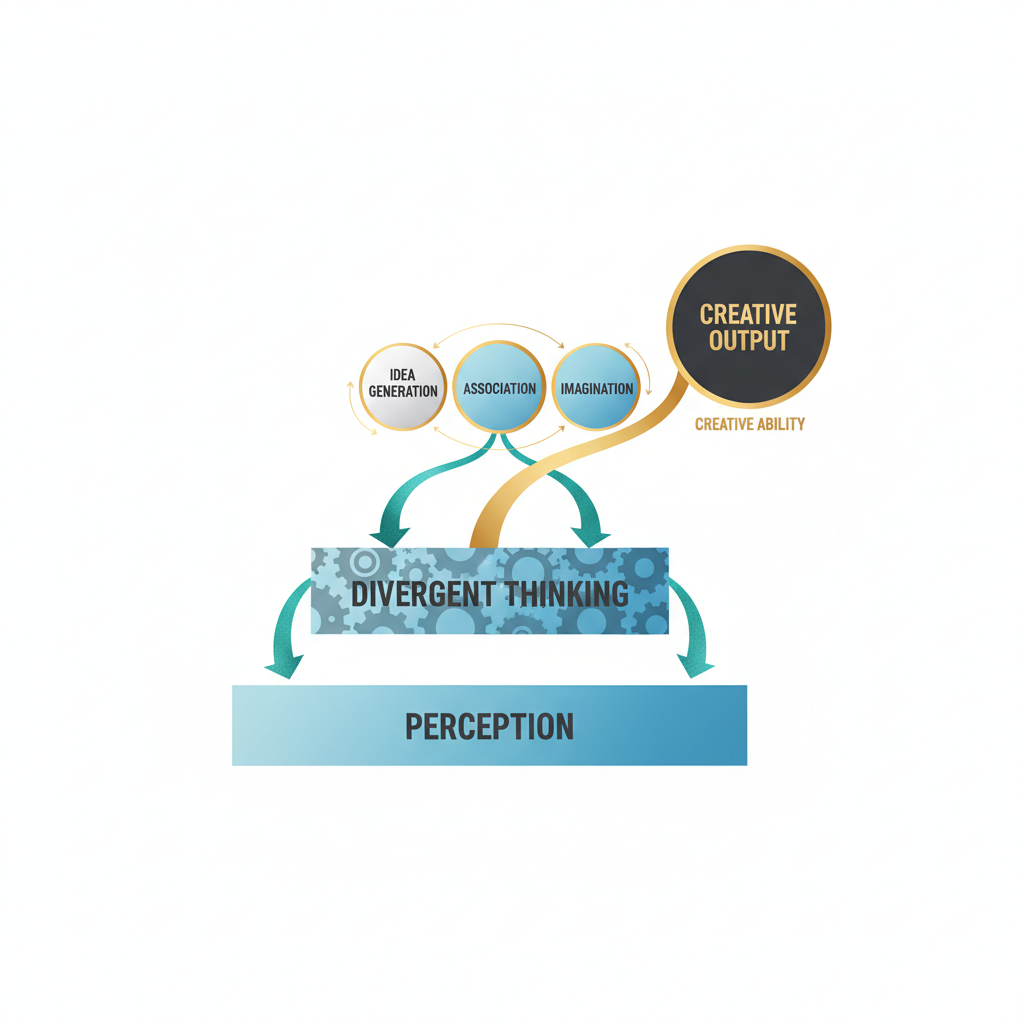
Creativity, for instance, is far too complex to be captured by one number. To understand your strengths, you need to look at the bigger picture. A multiple intelligence test offers this wider view. It helps you find your different talents, moving beyond just academic skills. This approach shows that people are smart and creative in many different ways.
This method highlights your different mental strengths. It reveals how different thinking styles help solve problems and drive innovation. Our platform, the Creative Ability Test, builds on this idea. We focus on how these different intelligences contribute to your unique creative potential.
Understanding Howard Gardner’s Theory of Multiple Intelligences
The idea of multiple intelligences changed how we view human potential. Dr. Howard Gardner, a psychologist at Harvard, introduced this groundbreaking theory. He argued that intelligence isn’t just one thing. Instead, he suggested that people have several different types of intelligence, and each one works mostly on its own.
Gardner’s first theory named seven intelligences, and this list later grew to nine. His work deeply changed education and psychology. It shifted our focus from a narrow idea of what it means to be “smart.” His theory suggests everyone is smart in their own way, which includes different kinds of creativity.
Understanding these different intelligences is powerful. It helps you see where your natural talents lie. For example, one person might be strong in Linguistic intelligence, while another might shine in bodily-kinesthetic intelligence. Both are valuable, especially for creative work. Knowing your main intelligences gives you a roadmap to use your strengths, solve problems better, and grow as a person.
The Creative Ability Test builds on this complete view. We help you discover how your specific intelligences shape your creativity. This gives you clear insights you can use to tackle real-world challenges.
Howard Gardner’s theory helps us appreciate different talents. It suggests that:
- Everyone has a unique mix of intelligences.
- These intelligences can be developed and made stronger.
- Knowing your mix helps you learn better and solve problems in new ways.
- Creativity isn’t just for artists. It’s a skill anyone can build on using their unique intelligences.
This wider view helps unlock your full potential and encourages you to embrace your unique ways of thinking.
What Are the 9 Types of Intelligence?
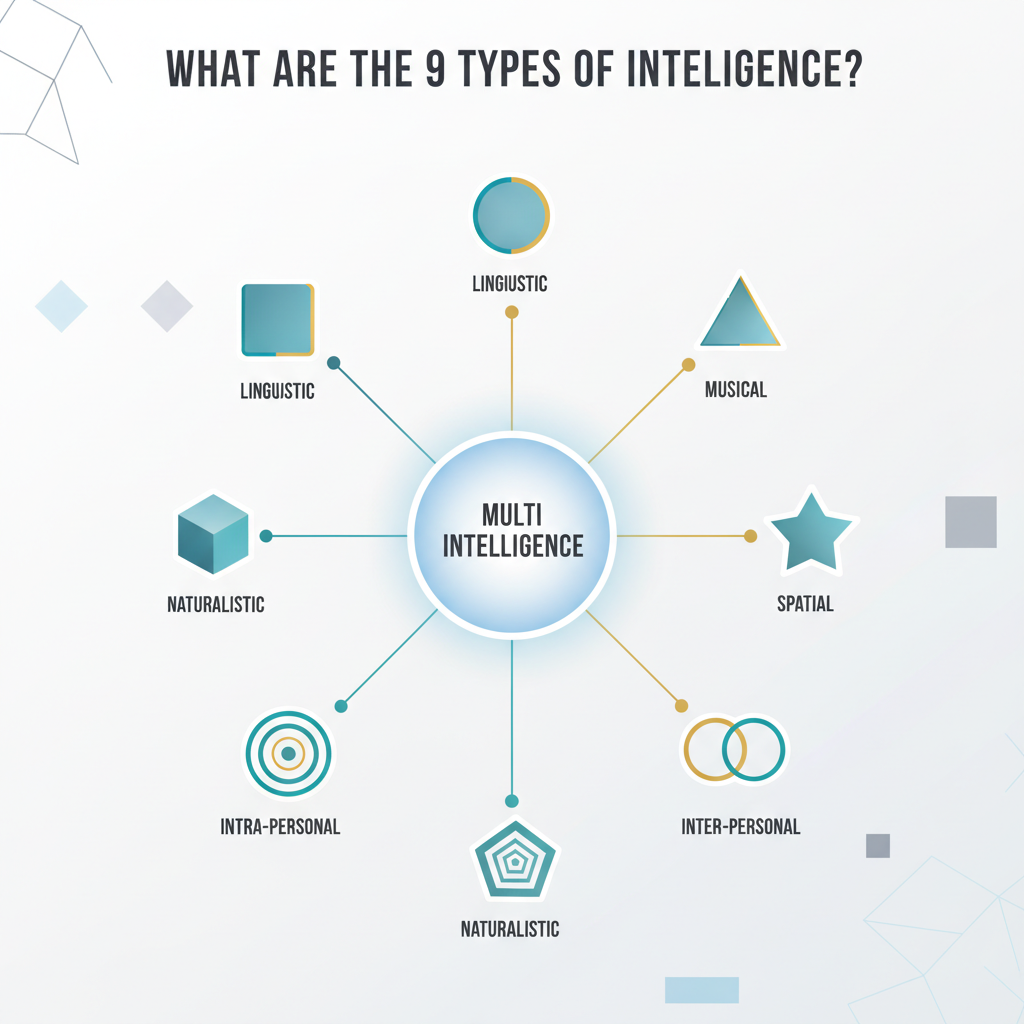
Knowing how people excel is a great way to unlock your own creativity. Howard Gardner’s Theory of Multiple Intelligences offers a wider view of what people can do [1]. It says intelligence isn’t just one thing, like an IQ score. Instead, it covers nine different types of strengths.
When you know these intelligences, you can find your natural talents. It also shows you the best ways to solve problems and create new things. Let’s explore each type and how it connects to your creative journey.
Linguistic Intelligence (Word Smart)
Linguistic intelligence is about being skilled with words. People with this strength love words. They are good at reading, writing, and speaking. They can explain their thoughts clearly and convincingly. Think of poets, novelists, or journalists.
How it fuels creativity: This intelligence is key for storytelling. It helps you create powerful stories. You can use words to express complex ideas. It helps you brainstorm and share new ideas well. It also helps you understand different viewpoints through language.
Develop your linguistic creativity:
- Read widely across different genres.
- Practice creative writing, even short stories or poems.
- Engage in debates or public speaking groups.
- Keep a journal to record your ideas and observations.
Logical-Mathematical Intelligence (Number/Reasoning Smart)
This intelligence involves logical reasoning. It includes seeing patterns and solving complex problems. People with this strength think logically. They enjoy abstract ideas and scientific questions. Scientists, engineers, and detectives often show high logical-mathematical intelligence [2].
How it fuels creativity: Creative problem-solving often relies on logical steps. This intelligence helps you break down challenges. It lets you create step-by-step solutions. You can break down big problems into smaller parts. This leads to new and effective results.
Develop your logical-mathematical creativity:
- Solve puzzles and brain teasers regularly.
- Explore coding or programming challenges.
- Practice critical thinking by evaluating arguments.
- Design experiments to test hypotheses, even simple ones.
Spatial intelligence (Picture Smart)
Spatial intelligence is the ability to see and understand the visual world. It involves changing what you see in your mind. People strong here can visualize objects and patterns. They have a good sense of direction and space. Architects, artists, and chess players often have high spatial intelligence.
How it fuels creativity: This intelligence is key for visual arts and design. It helps you imagine new products or spaces. You can move shapes and forms around in your mind. This leads to new ideas that look good and work well. It’s also key for understanding plans and visual messages.
Develop your spatial creativity:
- Engage in drawing, painting, or sculpting.
- Work on puzzles like jigsaw or 3D models.
- Study maps and practice navigating new places.
- Visualize your goals or solutions in your mind’s eye.
Bodily-Kinesthetic Intelligence (Body Smart)
This intelligence is about using your body skillfully. It involves coordination, balance, and skillful hand movements. People with this strength learn by doing. They often excel in physical activities. Dancers, athletes, surgeons, and craftspeople show this intelligence [3].
How it fuels creativity: Physical expression can be incredibly creative. This intelligence helps create new and interesting performances. It helps in designing products that are comfortable and easy to use. It also supports hands-on problem-solving. It’s about bringing ideas to life through movement and craft.
Develop your bodily-kinesthetic creativity:
- Participate in sports or dance.
- Take up a craft like pottery, woodworking, or knitting.
- Learn a new skill that requires fine motor control.
- Use gestures and movement to express ideas when speaking.
Musical Intelligence (Music Smart)
Musical intelligence is about being sensitive to rhythm, pitch, and melody. People with this strength enjoy and create music. They can recognize musical patterns easily. Composers, musicians, and singers have this natural gift.
How it fuels creativity: Music is a universal creative language. This intelligence helps you compose original pieces. It helps you perform with emotion. You can also use music to improve focus or set a mood for creative work. It’s a direct way to express emotion.
Develop your musical creativity:
- Learn to play a musical instrument.
- Experiment with composing simple melodies.
- Listen actively to diverse music genres.
- Notice rhythms and patterns in everyday sounds.
Interpersonal Intelligence (People Smart)
Interpersonal intelligence is the ability to understand others. It involves reading social cues and building relationships. People strong in this area are understanding and good communicators. Teachers, leaders, therapists, and negotiators often excel here.
How it fuels creativity: Working together is a powerful creative tool. This intelligence helps you work effectively in teams. You can gather different viewpoints. It helps create places where new ideas can grow. Understanding what people need leads to new solutions and better designs.
Develop your interpersonal creativity:
- Practice active listening in conversations.
- Participate in group projects and discussions.
- Volunteer for roles requiring teamwork.
- Seek out opportunities to mentor or be mentored.
Intrapersonal Intelligence (Self Smart)
Intrapersonal intelligence is about self-awareness. It means understanding your own emotions and motivations. People with this strength think deeply about themselves. They know their own strengths and limits. Philosophers, psychologists, and reflective artists often show high intrapersonal intelligence.
How it fuels creativity: Knowing yourself well is key to making honest, original work. It helps you find what you’re passionate about. You can set meaningful creative goals. It allows for honest self-expression in your work. This intelligence helps you use your unique ideas.
Develop your intrapersonal creativity:
- Practice mindfulness or meditation.
- Keep a reflective journal to explore thoughts.
- Set personal goals and regularly review them.
- Spend time in quiet contemplation.
Naturalist Intelligence (Nature Smart)
Naturalist intelligence involves understanding the natural world. This includes sorting plants, animals, and parts of the landscape. People with this strength observe patterns in nature. They appreciate and feel connected to their surroundings. Biologists, environmentalists, and farmers are good examples of this [4].
How it fuels creativity: Nature is an endless source of inspiration. This intelligence can lead to designs inspired by nature. It sparks ideas for long-lasting, eco-friendly designs. You can find ideas and comparisons in nature. It also encourages you to see the big picture when solving problems.
Develop your naturalist creativity:
- Spend time observing nature regularly.
- Learn about local flora and fauna.
- Engage in gardening or outdoor activities.
- Seek patterns and connections in the natural world.
Existential Intelligence (Life Smart)
Existential intelligence is about thinking about deep questions. These questions are about life, death, and why we are here. People with this strength look for meaning and purpose. They explore philosophical and spiritual ideas. Thinkers and spiritual leaders often display this intelligence.
How it fuels creativity: This intelligence can fill your creative work with deep meaning. It lets you explore experiences that all humans share. You can explore deep themes in art or writing. It encourages new ways of thinking about life’s biggest questions. This can lead to major new ideas in philosophy or art.
Develop your existential creativity:
- Engage in philosophical discussions.
- Reflect on your values and beliefs.
- Read literature that explores deep life questions.
- Seek out experiences that broaden your perspective.
Understanding these nine intelligences can have a big impact on your self-discovery. It helps you find your main strengths. This knowledge is very useful for personal and career growth. Our Creative Ability Test provides personalized insights into your unique thinking styles. It helps you leverage these strengths for innovation and problem-solving.
How Can a Multi Intelligence Test Benefit You?
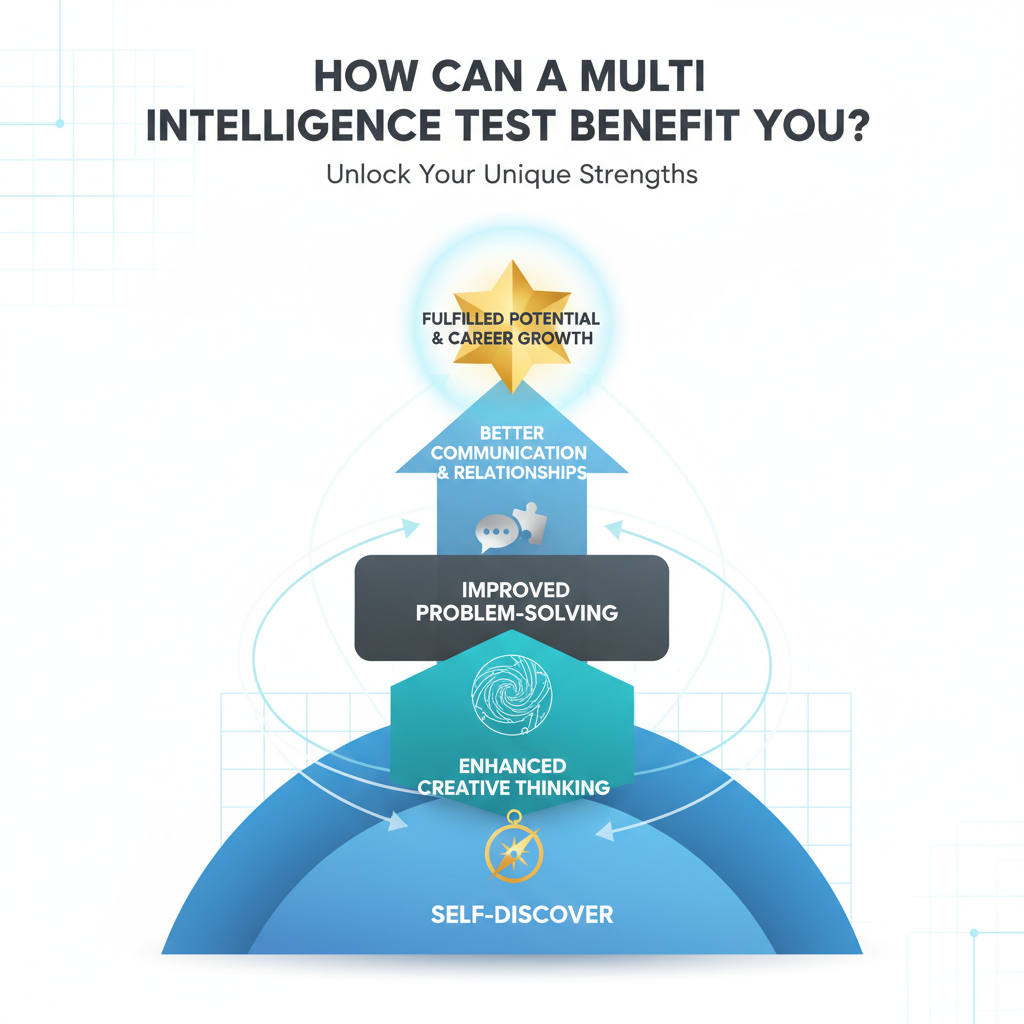
Enhancing Personal Growth and Self-Awareness
Understanding your unique intelligences is a powerful first step. It helps you see yourself beyond generic labels. A multiple intelligence test gives you a clearer picture of who you are.
This self-discovery helps you grow as a person. You’ll get a better sense of how you think and learn. It also reveals your natural creative talents. For instance, someone with high Spatial Intelligence might be great at visual problem-solving or graphic design. [5]
Knowing your strengths builds confidence. You learn to value your unique way of solving problems. This understanding can turn self-doubt into self-assurance. It confirms that your personal thinking style is valid, helping you become more comfortable with who you are.
Here are key benefits for personal growth:
- Discover Your Core Strengths: Find out where your natural talents lie, including the different ways you process information and share ideas.
- Uncover Creative Styles: Learn about your unique approach to creativity. Are you a logical thinker or an artistic one? Your results offer clues.
- Boost Self-Esteem: Understand your value and what you have to offer. This knowledge empowers you to make the most of your skills.
- Improve Decision-Making: Make choices that line up with your natural talents, whether in hobbies, learning, or personal projects.
- Become More Adaptable: See how your different intelligences work together. This can help you adjust to change and come up with new ideas.
The Creative Ability Test provides personal insights. It helps you connect your intelligence profile to your creative potential. This guidance gives you practical ways to understand yourself better.
Guiding Academic and Student Development
For students, understanding their intelligences can be a game-changer. It changes how they approach learning. This insight helps them match their study methods to their strengths. As a result, learning becomes easier and more enjoyable. [6]
For example, a student strong in Bodily-Kinesthetic intelligence might learn best with hands-on projects. Another student with high Linguistic intelligence learns best from reading and discussions. Recognizing these differences helps students succeed and reduces frustration with one-size-fits-all teaching methods.
A multiple intelligence test can also help students with problem-solving. They learn to use their specific strengths to tackle academic challenges. This encourages creative thinking from a young age. For instance, a student with spatial intelligence might use diagrams to solve math problems, which is a creative way to use their strength.
How this test supports students:
- Find Better Ways to Learn: Students can choose study methods that match their intelligence profile. This helps them remember information and understand it better.
- Improve Problem-Solving: Students learn to approach schoolwork using their unique mental strengths, which builds confidence in their abilities.
- Boost Academic Performance: Using study methods that fit them often leads to better grades and a deeper interest in their subjects.
- Develop Creative Thinking: Students discover how their intelligences drive creativity, which they can apply to projects and essays.
- Reduce Learning Frustration: When students understand why certain methods work for them, it creates a more positive learning experience.
The Creative Ability Test offers easy-to-understand results. It helps students see their scores clearly, empowering them to use these insights in their studies. This gives them a clear plan for academic success.
Boosting Professional Skills and Career Choices
In your career, understanding your intelligence profile is extremely useful. It helps you find work that matches your natural talents. This leads to greater job satisfaction, better performance, and more creative ideas. Many companies now see the value of having different types of intelligence on their teams. [7]
This knowledge helps you find the right career path—one that uses your best skills. For example, someone with high Interpersonal Intelligence might be great in a leadership role or in working with clients. A person with Logical-Mathematical strengths could succeed in data analysis or engineering. These insights help you build a more meaningful career.
These insights also improve teamwork. Knowing your coworkers’ strengths helps you assign tasks more effectively. It also creates a more creative and productive workplace. People with different intelligences bring unique points of view to problem-solving, which leads to better solutions.
Key professional advantages include:
- Smarter Career Planning: Make career decisions based on your natural abilities, which can open doors to more fulfilling jobs.
- Better Job Performance: Use your strengths to do better in your current role and find new ways to approach your tasks.
- Improved Teamwork: Understand how you contribute to a team and learn to value and use the different thinking styles of others.
- Encourage Workplace Innovation: Apply your unique creativity to solve problems, leading to new ideas and breakthroughs.
- Strengthen Leadership Skills: Learn how to motivate and communicate better by adapting your leadership style to different team members.
The Creative Ability Test gives you practical tips to improve your creative thinking. These skills are important for problem-solving and innovation at work. Discovering your strengths can lead to major career growth.
How Does Multiple Intelligence Connect to Creativity?

Creativity isn’t just one skill—it’s a process that uses many of your abilities. Howard Gardner’s theory of Multiple Intelligences offers a great way to understand this. It shows how different kinds of intelligence power your creative thinking. When you know your main intelligences, you can use your unique creative style to see problems in new ways and come up with truly innovative solutions.
Identifying Your Creative Thinking Style
Everyone has a unique mix of intelligences, and this mix shapes how you think creatively. Your strongest intelligences guide how you naturally come up with ideas, solve problems, and share your original thoughts.
For example, someone with strong word skills (Linguistic Intelligence) might be great at telling stories or writing persuasive proposals. On the other hand, a person with strong visual skills (Spatial Intelligence) might imagine new designs or figure out a complex puzzle by arranging its pieces.
Understanding your intelligence profile shows you where your creative strengths are. It points to the ways you’re most likely to have great ideas. Our science-backed Creative Ability Test helps you discover your unique style and gives you clear insights into how you naturally create. This self-awareness is the first step to reaching your full creative potential.
- Linguistic Intelligence: Creative storytelling, effective writing, persuasive communication.
- Logical-Mathematical Intelligence: Creative problem-solving, structured thinking, creating effective systems.
- Spatial Intelligence: Imagining new concepts, artistic expression, designing products and spaces.
- Bodily-Kinesthetic Intelligence: Expressive movement, hands-on building, creating original performances.
- Musical Intelligence: Composing new music, solving problems with rhythm, creative sound design.
- Interpersonal Intelligence: Creating ideas with others, guiding creative groups, creating solutions for people.
- Intrapersonal Intelligence: Self-reflection that sparks new ideas, ideas for personal growth.
- Naturalist Intelligence: Finding ideas in nature, sustainable design, understanding how systems work.
- Existential Intelligence: Asking big questions, imagining the future, developing new ways of thinking.
Using Your Strengths to Solve Problems
Once you know your key intelligences, you have a real advantage. You can intentionally use these strengths to tackle any challenge. This changes problem-solving from guesswork into a focused, effective process.
Imagine a team is having trouble communicating. Someone with strong people skills (Interpersonal Intelligence) might suggest new team activities or lead open discussions to help. In contrast, a person with strong logic skills (Logical-Mathematical Intelligence) might look at data to find the root of the communication problem.
Using your natural strengths makes you a much better creative problem-solver. It helps you come up with more original and effective solutions. The Creative Ability Test does more than just find your strengths; it gives you practical strategies. You’ll learn how to use your unique intelligence profile to solve real-world problems with confidence and fresh ideas.
For example:
- If you are “Body Smart,” you might build physical models or use role-playing to work through a complex process.
- If you are “Picture Smart,” sketching diagrams or mind maps can help you sort through complex ideas.
- If you are “People Smart,” you could get others involved in brainstorming to use the group’s collective intelligence.
Moving from Intelligence to Innovation
Think of intelligence as your raw material, creativity as the engine, and innovation as the final product. Innovation is what happens when you successfully use a new, creative idea. Knowing your Multiple Intelligences is key to innovating again and again. It helps you find new solutions that have a real impact.
Turning your potential into real change is a personal journey that starts with knowing how your mind works. For example, someone with strong self-awareness (Intrapersonal Intelligence) might create new self-help programs based on their own insights. In the same way, someone with a strong connection to nature (Naturalist Intelligence) could develop new ideas for protecting the environment [5].
The Creative Ability Test is designed to guide you on this journey. It helps you turn your natural intelligences into real-world innovations. With our personalized feedback and practical tips, you’ll learn how to develop your own creative style. This turns your mental strengths into skills you can use. You’ll go from just knowing your potential to actively creating your future. Our platform helps you use creativity to grow professionally and find personal satisfaction.
What to Look For in a Kinds of Intelligence Test Online?
Ensuring the Test is Comprehensive
When you look for an online intelligence test, a complete one is best. A good test does more than give you a quick summary. It should check many of your different mental skills. This means it needs more than just simple questions or short quizzes.
Look for tests that are based on proven science. For example, Howard Gardner’s theory of multiple intelligences is a well-known model. Tests like this give you a full picture of your abilities. They should also have enough questions to be useful. Our Creative Ability Test has 30 questions, which helps us understand your unique ways of thinking.
A complete test shows you all the different sides of your strengths. It helps you see how they add up to your total creative skill. A test based on science also gives you trustworthy results. It won’t give you vague feedback. Instead, you get a clear picture of your many talents. This is the best way to truly understand yourself and grow.
Seeking Actionable Insights, Not Just Labels
Getting a label like “word smart” or “picture smart” is a good start. But a really good intelligence test gives you more. You need useful advice you can act on. Look for tests that offer feedback made just for you. This feedback should clearly explain what your results mean for you.
A good test won’t just put you in a box. It should give you clear ways to improve and grow. For example, it’s helpful to know you have strong spatial skills. But it’s much more useful to know how to use that skill to picture hard problems. A great test shows you how to build on your strengths and use them in your daily life.
This helps you move from just knowing about your skills to actually using them to grow. Our Creative Ability Test is designed to give you this kind of useful advice. We help you turn what you learn about yourself into real-life improvements. This allows you to build your creative skills in a smart, focused way.
Connecting Your Results to Real-World Application
The main goal of any intelligence test is to help you in real life. Your results shouldn’t just be numbers on a screen. They should help you make better choices. A great test connects your strengths to everyday situations. Think about how your strongest skills can improve your life at home and at work.
For example, good people skills can help your team be more creative together. Or, a logical mind can make solving problems at work easier. The right test gives you clear examples. It shows you how to use your unique skills well. This might help you choose a better career path [8] or find new ways to study.
Plus, when you understand your strengths, you can be more innovative. Knowing how you like to think helps you solve problems in new ways. Our platform gives you these real-world strategies. We connect knowing yourself with growing as a person. This helps you use what you’ve learned for everything from daily tasks to your biggest goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 8 types of intelligence test?
Howard Gardner’s influential theory of Multiple Intelligences says that intelligence isn’t just one single skill. Instead, it’s made up of several different types. He started with seven, later adding an eighth and a ninth. So, when people talk about the “8 types of intelligence,” they usually mean his most well-known ideas.
A multiple intelligence test measures your strengths in these different areas. This helps you understand your unique way of thinking. Our Creative Ability Test, for example, explores how your natural strengths can affect your creative thinking and problem-solving styles.
Here are the eight main types of intelligence:
- Linguistic Intelligence: Skill with words, language, and writing.
- Logical-Mathematical Intelligence: Ability to reason, do math, and think in abstract ways.
- Spatial Intelligence: Ability to visualize, think in 3D, and understand spaces.
- Bodily-Kinesthetic Intelligence: Skill in using your body with control and precision.
- Musical Intelligence: Sensitivity to rhythm, pitch, melody, and sound.
- Interpersonal Intelligence: Understanding and working well with other people.
- Intrapersonal Intelligence: Understanding yourself, your emotions, and what motivates you.
- Naturalist Intelligence: Recognizing and sorting patterns found in nature.
Knowing your strongest intelligences can help you improve your creative skills. For instance, strong spatial intelligence can lead to new design ideas, while linguistic intelligence can help you tell great stories. Our platform helps you turn these strengths into practical creative strategies.
How is a personality intelligence test different?
It’s important to know the difference between intelligence and personality. Intelligence tests, like those based on Gardner’s theory, measure your thinking skills. They look at your ability to learn, reason, and solve problems in different areas.
Personality tests, on the other hand, look at your typical patterns of thinking, feeling, and behaving. They show your personal traits, preferences, and social styles. Examples include tests for introversion/extraversion or conscientiousness.
Even though they are different, intelligence and personality are connected. Personality traits can have a big impact on how you use your intelligence. For example, people high in “openness to experience” (a personality trait) often score higher on creativity tests [9]. This trait is linked to curiosity and a desire to explore new ideas.
Our Creative Ability Test focuses on your potential to be creative. It looks at your ability to think flexibly and come up with many ideas, which are key parts of intelligence. It also explores if your approach to problems matches creative ways of thinking. This gives you personal insights, showing you not just what you can do, but how your unique style can help you be more innovative.
Can I find a multiple intelligence test for students?
Yes, multiple intelligence tests are widely used and very helpful for students of all ages. Teachers often use these tests to better understand how each student learns. This helps them match their teaching methods to what students are good at.
For students, understanding their main intelligences can make a big difference. It helps them choose school subjects that fit their natural talents. It also helps them find better ways to study. For example, knowing you are strong in spatial intelligence might encourage you to use more charts and diagrams.
Our platform connects this to creativity by helping students use their strengths to be more creative with schoolwork. It guides them to think of new ideas for projects and problems. This encourages a growth mindset and builds confidence for the future. Discovering your unique creative style early on can be a great start for personal and professional growth.
What is an interpersonal intelligence test?
An interpersonal intelligence test looks at how well you understand and work with other people. This type of intelligence is often called being “people smart.” People with this strength are good at noticing the moods, goals, and feelings of others. They do well in social situations.
Key signs of strong interpersonal intelligence include:
- Great communication skills, both spoken and unspoken.
- A high level of empathy and sensitivity to others.
- The ability to build connections and keep relationships strong.
- Strong leadership and teamwork skills.
- Skill in solving conflicts and guiding discussions.
While our Creative Ability Test measures your creative thinking and problem-solving, interpersonal intelligence is very important for using creativity in the real world. New ideas rarely happen when you work alone. Working with others on creative projects, leading teams, and understanding customer needs all require strong people skills. Learning about your core creative strengths helps you share your ideas more effectively. It also helps you inspire and work with others on your creative projects.
Sources
- https://www.niu.edu/facdev/resources/guide/learning/howard-gardners-theory-of-multiple-intelligences.shtml
- https://www.tec.edu.mx/en/news/campussur/careers-strong-mathematical-logical-intelligence
- https://howardgardner.com/multiple-intelligences/body-kinesthetic-intelligence/
- https://psychology.jrank.org/pages/426/Multiple-Intelligences.html
- https://howardgardner.com/multiple-intelligences/
- https://www.edutopia.org/multiple-intelligences-theory
- https://hbr.org/2011/04/the-power-of-multiple-intelligences
- https://www.careerkey.org/multiple-intelligences-theory-careers
- https://psycnet.apa.org/record/2012-07310-001